Get in touch
Email: info@empoweringabilityjourney.com.au
Phone: 0451 093 210 or 1300 045 841
Preventing Problems Before They Start
Complex Wound Care - Management and Prevention Strategies
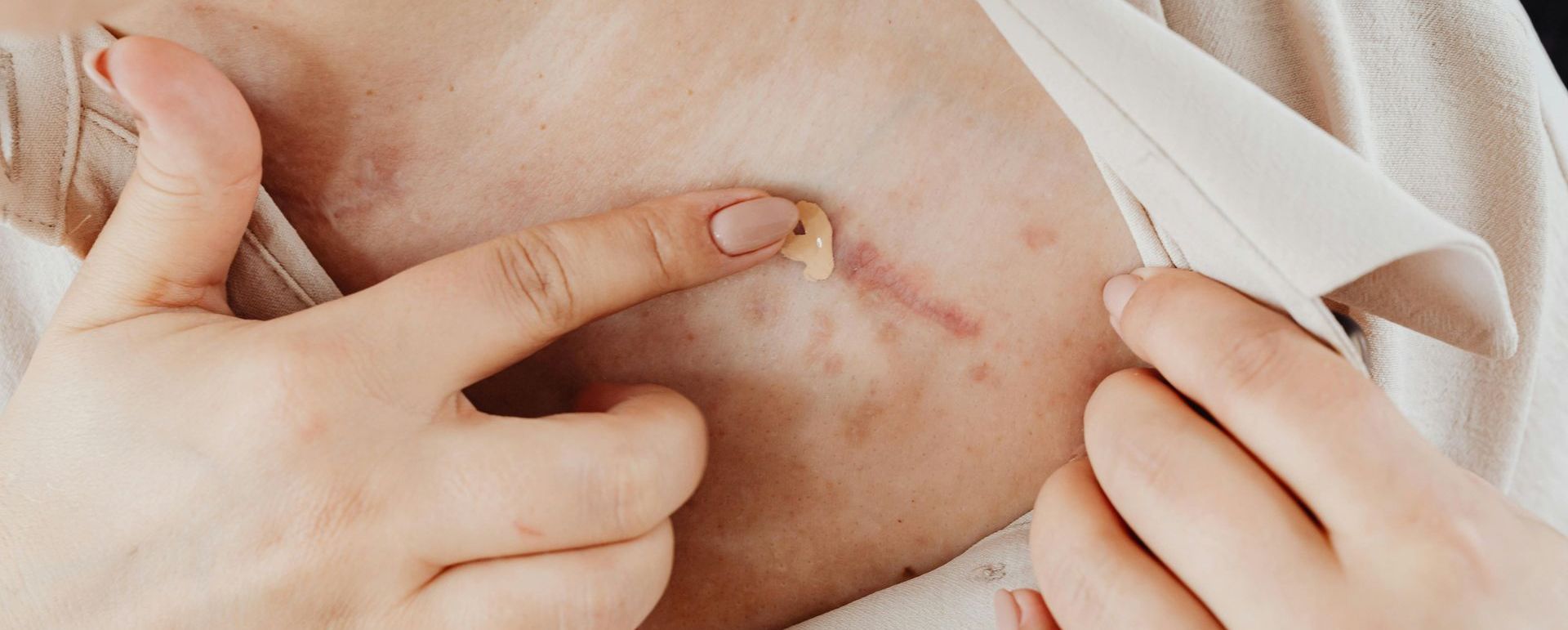
Wound care is a key part of healthcare. It focuses on treating and preventing injuries to the skin or tissue. Wounds can be acute, like cuts or burns, or chronic, like pressure ulcers or diabetic wounds.
Chronic wounds need specialised care due to delayed healing, requiring tailored care plans.
Understanding Wound Classifications: A Simple Guide
Acute Wounds
Burns: Caused by heat or chemical exposure.
Cuts and Abrasions: Skin damage from physical trauma.
Chronic Wounds
Pressure Injuries/Ulcers: Damage caused by prolonged pressure or friction, often over bony areas.
Diabetic Wounds: Persistent wounds linked to diabetes complications.
Surgical Wounds / Skin Tears
These occur after medical procedures or trauma to delicate skin. Proper care prevents complications and supports healing.
Nha's Advice on Nutrition for Healing
Eating foods rich in protein, like eggs and beans, can help your wounds heal faster.
A balanced diet gives your body the strength it needs to recover.
Nha's Advice on Nutrition for Healing
Eating foods rich in protein, like eggs and beans, can help your wounds heal faster.
A balanced diet gives your body the strength it needs to recover.
How to Get Wound Care Right Every Time
Comprehensive Assessment
Check the wound and the person’s overall health to spot healing barriers. Document findings and update care plans regularly.
Personalised Care Plans
Create care plans that suit the individual’s needs and wound type. Use proven treatment protocols for the best results.
Effective Treatment Protocols
Select dressings that support healing and prevent infection. Reassess the wound often and adjust care plans as needed.
Infection Control
Follow hygiene practices to lower infection risks. Teach patients and caregivers to keep wounds clean and recognise infection signs like redness, swelling, or bad smells.
Holistic Support
Address physical, emotional, and mental needs. Involve the person in their care to ensure comfort and understanding.
The Best Ways to Prevent Issues
Early Detection
Check wounds often to catch potential issues early.
Pressure Injury Prevention
Use pressure relief devices, reposition frequently, and maintain proper skin care.
Nutritional Support
Promote healing with a balanced diet that meets the person’s needs.
Education
Train staff, patients, and caregivers on wound care practices and warning signs.
Do’s and Don’ts in Wound Management
Do’s
- Assess the wound and overall health regularly.
- Use proven treatment methods for specific wounds.
- Keep strict hygiene to prevent infections.
- Adjust care plans as the wound changes.
- Teach patients and caregivers about wound care.
- Address conditions that delay healing.
- Encourage teamwork between healthcare staff and families.
Don’ts
- Ignore infection signs or delay treatment.
- Use unsuitable dressings that may harm the wound.
- Neglect hygiene or fail to help with care.
- Stick to outdated care plans without updates.
- Focus only on the wound without considering overall health.
Why Wound Care Matters
Wound care needs a patient-focused approach. It includes proper assessment, infection control, and personalised care.
Addressing physical and emotional needs helps prevent complications and supports recovery. Regular checks, education, and collaboration are key to long-term healing and better outcomes.
Ready to Improve Wound Care?
Contact our team today to learn more about effective wound care practices.
Expert guidance is just a call away to help you or your loved ones heal safely and comfortably.
Send Us a Message
Contact Us
We will get back to you as soon as possible.
Please try again later.
Loved and recommended by Athletic Koala NDIS Website Team

